At the beginning of the class, we did the Charge Buildup and Decay in Capacitors in this photo
we use two bulbs , 2 capacitors, 6 wires . to answer the questions.
in this photo, we first make a circle of a battery, a capacitor and a swith in series. When we close the swith, the bulb gets dimer and dimer and finnally it is not bright., the graph is on the photo.
Then we take away the battery and make the circle of just battery and capacitor in series,. and we saw that the bulb lights again, then it gets dimer.
In this photo, we draw a sketch of the brightness of the bulb and the time when it is placed across a charged capacitor without the battery present.
It is a non-line graph. at first, the time is 0, the bulb is most brightness, then as time increases, the bulb gets dimer and dimer.
in this photo, we first use different batteries to charge two capacitance and then make them like the graph in the fist photo, and measure their voltage.
In the second photo, on the left, it is our prediction. we think when we make the two capacitance together, the voltage should become 1V. But when we measure them, the voltage is just the average of them.
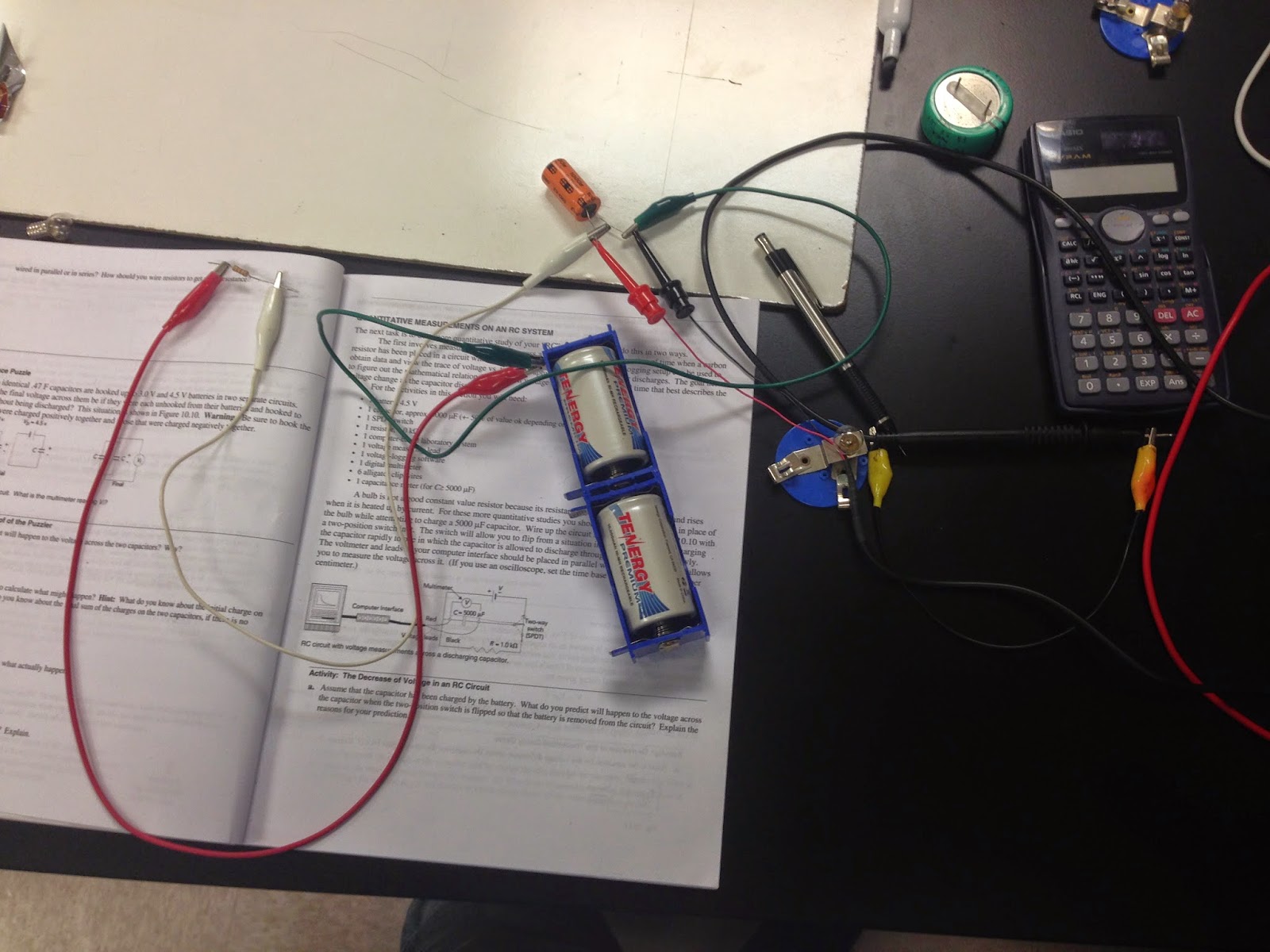
In this photo, we begin to make the experiment about Quantitative Measurements on An RC System.
We use a battery, a capacitor, a resistor, a voltage measuring lead, the computer, 6wires.
This is what we make like the graph on the lab manual.
in this photo, we use logger pro to measure the two process, one is charge the capacitor, another is discharge the capacitor. The red one is charge, blue one is discharge.
In this photo, we use the equation V=IR, Q=CV to find the unit of RC, and we know the unit of I is c/s, and find the unit of RC is s(seconds).
in this photo, we use the equation V=Q/C,V=IR and I=dq/dt,to find dq/dt=-q/RC, and then we intergo both sides and find q=e^(-t/RC)
In this photo, professor made an experiment to show us, when turn on the green box, the two wires together will explode.
In this photo, if we only know the two graphs on the left, what can we get the graph of I vs t?
Because the voltage is increased by the time, and Brightness decreases by the time, we know Brightness decreases means the power is decreased, so according to equation P=IV, P decreases, V increases, we get that I should decrease.
Then we did a RC circuit problem in the photo
We use the two equations on this photo, one is charge, another is discharge.
First, we should find the RC in the photo, and we get that RC is 1s, another loop's RC is 0.
Then we just use Q=CV to find the Q, and we know the voltage of resistance is 1.5V, we use the equation of charge to find the t is 1.1s.
Then in this photo, when we turn off the switch, we will find that RC=3.5s, and we use the equation of discharge to find the time is 149s.
Conclusion:
In today’s class, we analyze
the idea of capacitors and the charge buildup and discharging of capacitors in
a circuit. We did many experiments on capacitors to understand how they work,
and how they affect a circuit. We know that what happens when connected in
series or parallel, and we did experiments at the different types of RC
circuits about developing a relationship between their charging and
discharging. At the end of the class we did
some excises to calculate capacitance, time constants, and maximum charge of a
circuit