The first one is the bin before magnetizing, the particles in the bin are chaotic, so the net force can be canceled.
The second one is the bin after magnetizing. Through magnetizing, the particles in bin are all well-organized, so it can show the north and south poles.
in this photo, we think about two ways to destory a magnet. one is heating and another is hitting it.
Then in these two photos, the professor heats the bin and show us the result, and we find that after heating the bin, it doesn't have magnetism and it can't change the direction of compass.
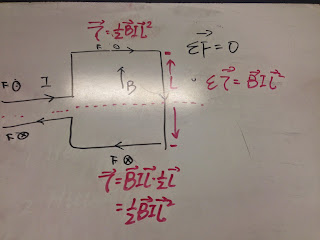
In this photo, we begin to do another exercise, make the loop galvanical and give it a magnet field, the direction is upward. Then we find that only the top and bottom lines has Force and the net force is 0.
Then we use the equation torque=F*r ,and F=BIL to find the torque=1/2BIL^2, and the net torque is BIL
In this photo, we use the three equation in yellow to answer the question of the example at the bottom.
in this photo, we use the equation torque=NIABsin(theta) to find the torque , we need to be careful that the theta should be 60, not 30.
Then the professor change the rectangle to circle. the equation is same:torque=NIAB=1885N*m
in this photo, the professor shows us motor in parts.
There are three ways to break a motor, the first one is brushes, the second one is commutator, and the last way is coil contract fails.
Then we start to do the experiment about electric motor, we use a battery, two fixed contacts and a split ring commutator to complete this experiment
in this photo, we draw four situations about the motion of electric motor, the top two have same direction of current, but the different direction of magnet field. The left two have same direction of magnet field, but direction of current.
We found that when we change the direction of current or the direction of magnet field, the direction of rotation would change.
Then we answer the question on the lab manual.
Then we made a simple electric motor by ourselves. We use small gauge enamel coated wire, two large paper clips, block of wood ,magnet, power supply and two alligator clip connectors.
This is the video we made and shows the success of this small electric motor.
in this photo, we use the equation E=VB, E=V_h/W and I=roh*q*V*W*t to find the V_h=BI/roh*q*t
The professor makes a galvanical wire in the middle, before closing the switch of the battery, we observe that all compass are direct to north
In this photo, we predict after closing the switch of the battery, what will happen. and we guess that the north of compass will direct in a circle.
in this photo, the professor shows us the result of this experiment and our predict is correct.
In this photo, the professor changes the direction of current and we find that all compass's north direct an opposite direction., but still form a circle,
In these two photos, the professor let us predict the direction of north pole of three compass and we draw the graph on the second photo.
in this photo, we find the equation of B
in this photo, we get the relationship between the Force of Magnet field and the force of electric field is about the velocity of light and the speed of particle.
Conclusion:
In today’s class, we
learned a lot about magnetism and the properties that are inside the magnets
and how they interact with the other. We learned that torque is generated
in a current loop in a magnetic field due to forces on the sides when there are
N turns of wire. We learned about another right hand rule which shows us the
direction of the magnetic field. We learned how to create a magnet and
how to destroy a magnet. We were also introduced to motors and use magnetic
fields to rotate the motor. We also created a motor with a wires, paper clips,
and a battery.






















No comments:
Post a Comment